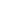
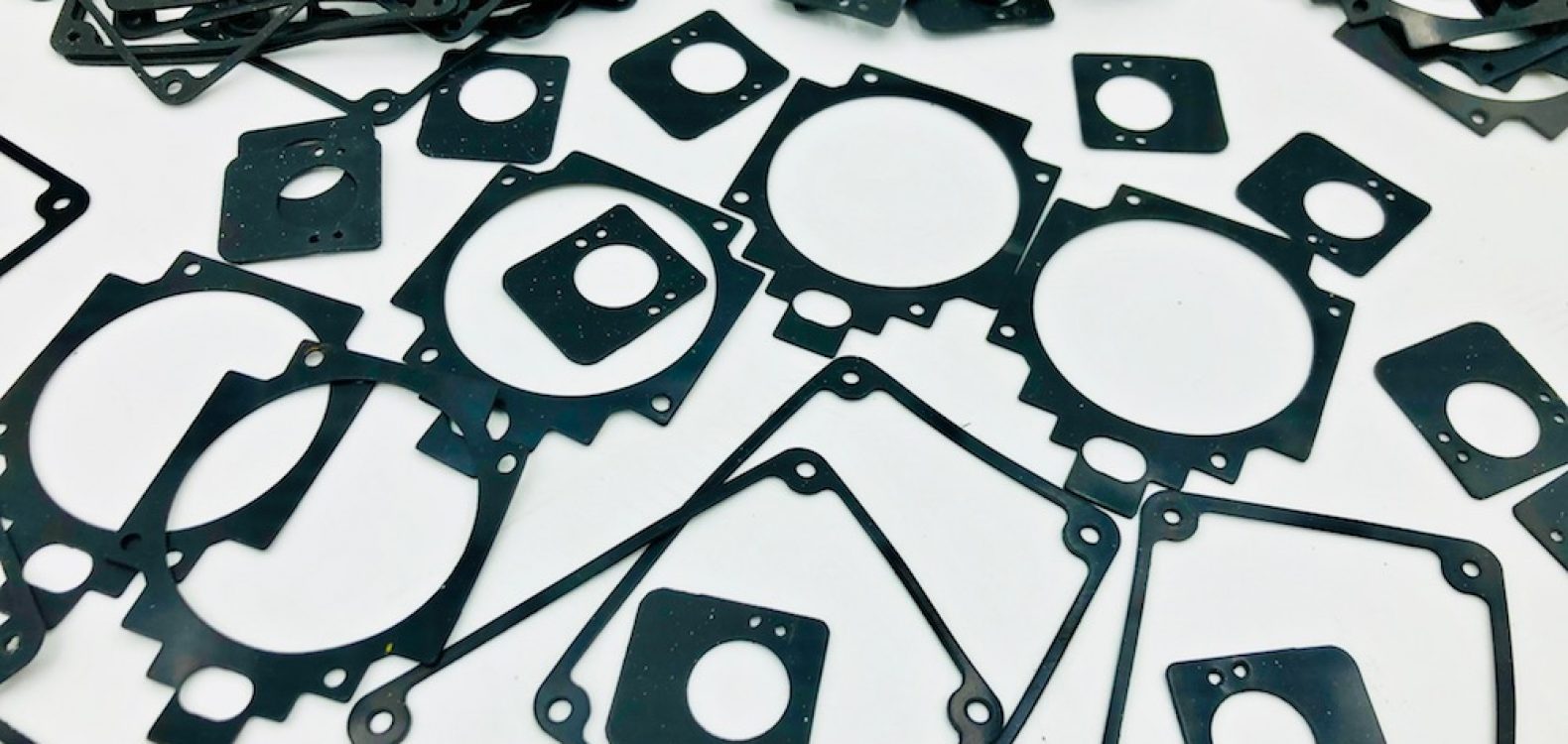
Industrial seals are essential components in various industrial applications, serving the critical function of preventing leakage, protecting machinery, and ensuring the reliable operation of equipment and systems. These seals come in a wide range of designs and materials, tailored to the specific requirements of different industries. In this comprehensive description, we’ll explore the various aspects of industrial seals, including their types, functions, materials, and applications.
Purpose and Function:
Industrial seals are primarily designed to provide a barrier between different components, fluids, or environments to achieve the following functions:
- Leak Prevention: The primary purpose of industrial seals is to prevent the escape of liquids, gases, or solids from a confined space. They create a physical barrier to maintain the integrity and safety of a system.
- Contamination Control: Seals play a crucial role in preventing contaminants, such as dust, dirt, and foreign particles, from entering sensitive equipment or processes, thus ensuring the quality and performance of products.
- Friction Reduction: In applications involving moving parts, seals help reduce friction and wear by providing lubrication and maintaining a film of fluid between surfaces. This is particularly important in machinery like pumps and bearings.
- Environmental Protection: Industrial seals protect equipment from adverse environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, corrosive substances, and high pressures, ensuring the durability of components.
- Safety: Seals are essential for maintaining the safety of industrial processes, especially in applications involving hazardous materials, as they prevent leaks that could lead to accidents or environmental damage.
Types of Industrial Seals:
- O-Rings: These are the most common type of seals and are used in a wide range of applications. O-rings are circular rubber or elastomeric seals that create a seal by fitting into a groove between two parts. They are effective in preventing leakage in both static and dynamic applications.
- Gaskets: Gaskets are flat, sheet-like seals used to create a barrier between two surfaces. They are often made of materials like rubber, cork, or metal and are commonly used in flanged connections.
- Lip Seals (Oil Seals): Lip seals are used to prevent the leakage of oil and other fluids in rotary shafts or axles. They have a flexible lip that comes into contact with the rotating shaft, creating a seal.
- Mechanical Seals: These are used in rotating equipment such as pumps and compressors. Mechanical seals consist of two sliding surfaces that create a dynamic seal to prevent leakage.
- Hydraulic Seals: Hydraulic seals are designed for use in hydraulic systems and are typically used in cylinders and other components. They come in various shapes and materials, including piston seals, rod seals, and wiper seals.
- Pneumatic Seals: Pneumatic seals are used in air-powered systems and serve a similar purpose as hydraulic seals. They prevent air leakage and come in different configurations for cylinders, valves, and other components.
Materials for Industrial Seals:
The choice of material for industrial seals depends on the specific application and its operating conditions. Common materials include:
- Elastomers: These are rubber-like materials such as nitrile, silicone, EPDM, and Viton, which are known for their flexibility, resilience, and resistance to various fluids and temperatures.
- Metal: Metal seals, often made of stainless steel or copper, are used in high-temperature, high-pressure applications, such as in the aerospace and petrochemical industries.
- Plastics: Some seals are made from plastic materials like PTFE (Teflon), which offer excellent chemical resistance and low friction properties.
- Composite Materials: These are combinations of materials designed to provide specific properties, such as enhanced wear resistance and improved sealing capabilities.
Applications:
Industrial seals find applications in a wide range of industries, including:
- Oil and Gas: Seals are used in drilling equipment, pipelines, and refining processes to prevent leaks and maintain safety.
- Automotive: In vehicles, seals are present in engines, transmissions, and various mechanical components to prevent fluid leakage and ensure smooth operation.
- Aerospace: Aircraft and spacecraft rely on seals to maintain cabin pressure, protect sensitive instruments, and ensure safe flight.
- Manufacturing: Seals are used in manufacturing machinery to prevent contamination, reduce friction, and maintain precise tolerances.
- Pharmaceuticals: Industrial seals play a crucial role in pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment to prevent contamination and maintain product purity.
- Food and Beverage: In the food industry, seals are used in processing equipment to ensure sanitary conditions and prevent product contamination.
- Mining: Seals are employed in mining equipment to protect against abrasive materials and harsh environmental conditions.
- Renewable Energy: Seals are used in wind turbines, solar panels, and hydropower systems to maintain efficiency and prevent environmental impact.
In conclusion, industrial seals are vital components across numerous industries, ensuring the reliability, safety, and efficiency of various processes and systems. Their diverse types and materials make them adaptable to a wide range of applications, from automotive to aerospace, manufacturing to energy production, and beyond. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of industrial seals are essential for the optimal performance of industrial equipment and systems.