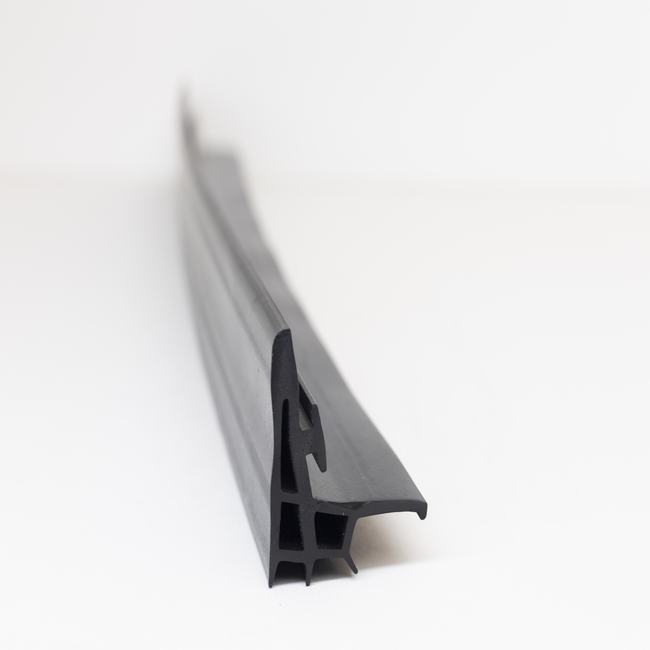
Dilatation seals, often referred to as expansion joints or expansion seals, are critical components in engineering and construction designed to accommodate thermal, structural, and seismic movements within structures and systems. These seals are employed to provide flexibility, absorb vibrations, and prevent damage or failure caused by the expansion and contraction of various materials and structures due to changes in temperature, pressure, or dynamic forces.
The primary function of dilatation seals is to maintain the integrity and functionality of a system or structure by effectively sealing gaps or joints while allowing for controlled movement. Here’s a detailed description of dilatation seals:
- Purpose and Function:
- Thermal Expansion: Dilatation seals are crucial in situations where temperature fluctuations can lead to the expansion and contraction of materials. They provide a means to accommodate these changes without causing structural damage or leaks.
- Structural Movements: Buildings, bridges, pipelines, and other structures can experience various types of movements, including settlement, settlement, and seismic activity. Dilatation seals are used to absorb and distribute these movements, reducing the stress on the structure.
- Vibration and Noise Reduction: In industrial and transportation applications, dilatation seals can also serve to dampen vibrations and reduce noise caused by machinery, traffic, or other sources of dynamic loads.
- Water and Gas Tightness: In many cases, dilatation seals must maintain water and gas tightness to prevent leakage or contamination. This is crucial in infrastructure like tunnels, dams, and water treatment facilities.
- Types of Dilatation Seals:
- Rubber Expansion Joints: These are often used in pipelines and HVAC systems to absorb vibration and movement. They are made of elastomeric materials like EPDM, neoprene, or natural rubber.
- Metal Expansion Joints: Metal bellows or corrugated metal expansion joints are used in high-temperature and high-pressure applications, such as in power plants, petrochemical facilities, and industrial processes.
- Fabric Expansion Joints: These are composed of fabric-reinforced materials and are often used in exhaust systems, flue gas ducts, and other applications that require flexibility while maintaining a gas-tight seal.
- Slide Bearings: Slide bearings are used in structural applications to allow for horizontal movement between components while maintaining vertical load support. They are commonly used in bridges and buildings.
- Design Considerations:
- Material Selection: The choice of materials depends on the specific application, considering factors like temperature, pressure, chemical exposure, and abrasion resistance.
- Mounting and Attachment: Dilatation seals must be securely attached to the adjacent structures to ensure they function as intended and accommodate movements without damage.
- Size and Movement Capacity: The size and movement capacity of the expansion joint must be carefully calculated to match the anticipated movement and requirements of the system or structure.
- Maintenance and Inspection:
- Dilatation seals require periodic inspection to ensure they are functioning correctly. This includes checking for signs of wear, damage, and proper sealing.
- Importance in Infrastructure:
- Dilatation seals are vital in infrastructure projects such as bridges, roads, tunnels, and buildings to ensure their longevity and safety. They help protect against structural damage and maintain the integrity of these critical components.
In summary, dilatation seals are essential elements in various engineering and construction applications, serving to accommodate thermal, structural, and dynamic movements while maintaining the integrity, safety, and functionality of systems and structures. Their design, material selection, and installation must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity.